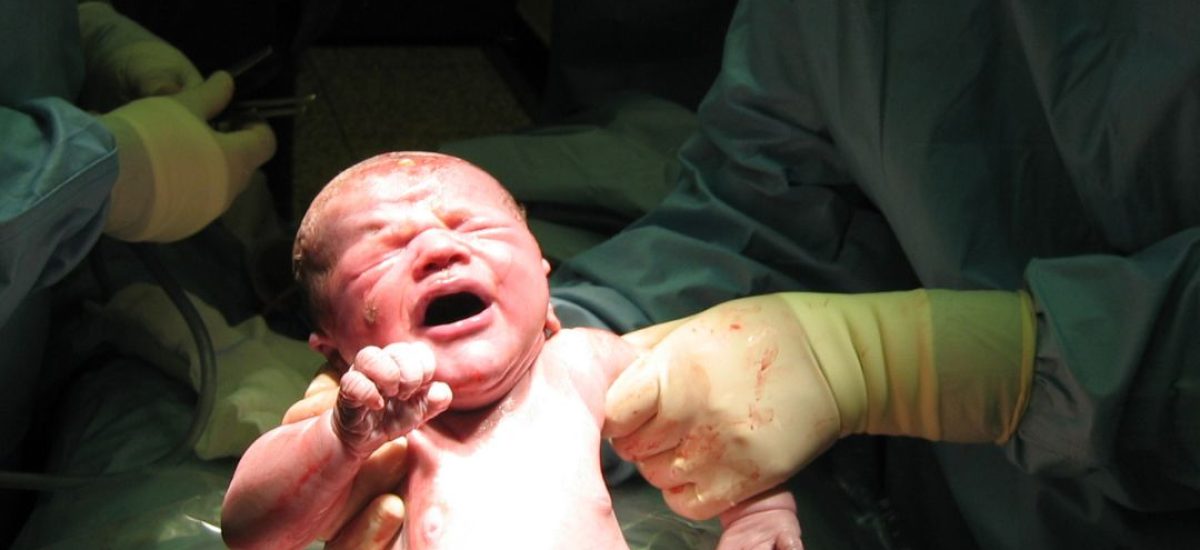
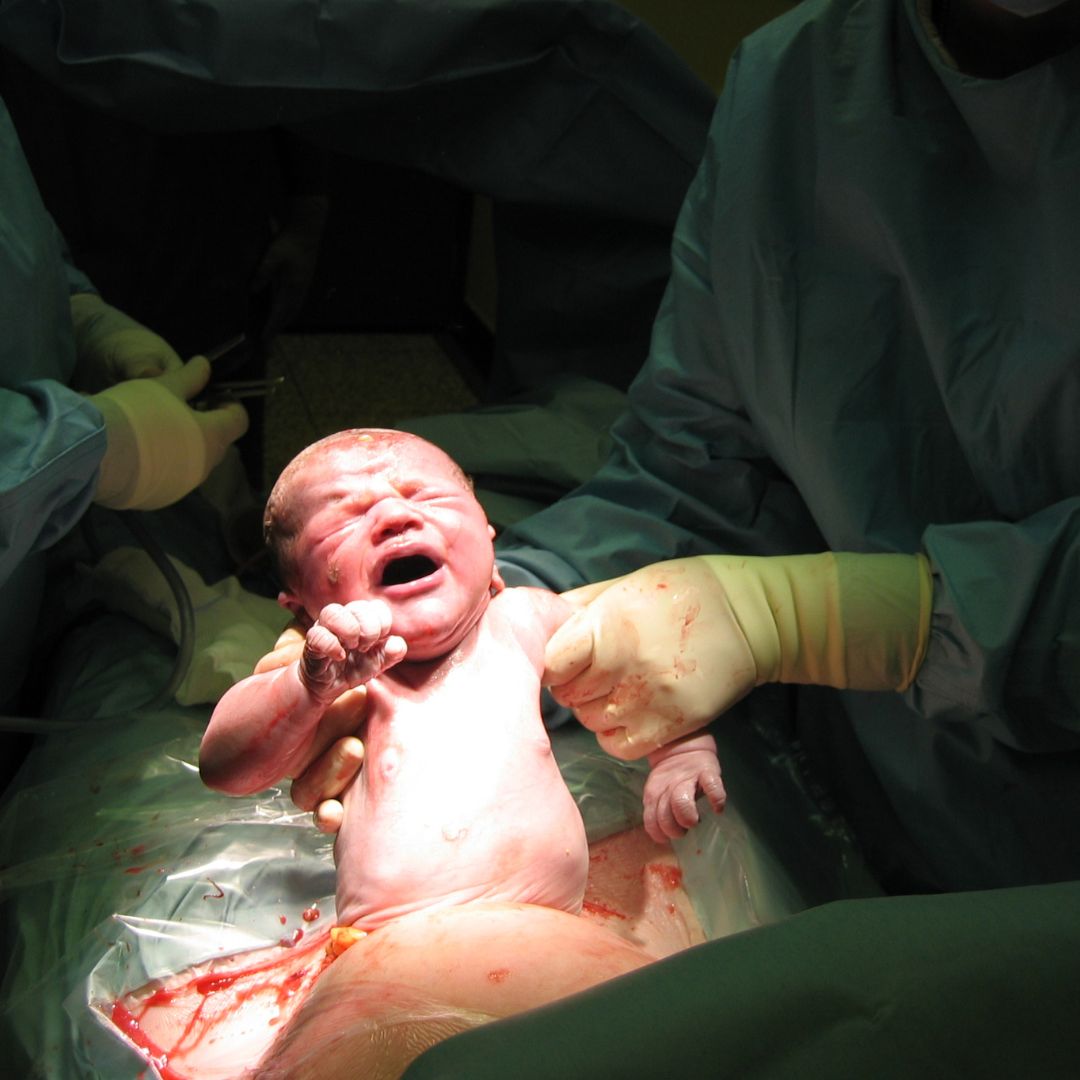
Both normal (vaginal) delivery and Caesarean section (C-section) are methods of childbirth, and each has its own processes, benefits, and considerations. Here’s a detailed overview of both:
Normal (Vaginal) Delivery
Definition:
- A vaginal delivery is the process of giving birth through the birth canal. It is the most common method of childbirth.
Process:
- Labor:
- Early Labor: Contractions begin and may be irregular. The cervix starts to dilate (open) and efface (thin out).
- Active Labor: Contractions become more frequent and intense. The cervix dilates more rapidly to 6-10 cm.
- Transition Phase: The most intense phase of labor, where the cervix completes dilation to 10 cm.
- Delivery:
- Pushing: Once fully dilated, the mother begins to push with contractions to help the baby move through the birth canal.
- Birth: The baby is born through the vagina, and the umbilical cord is cut after delivery.
Benefits:
- Shorter Recovery Time: Generally, recovery is faster compared to a C-section.
- Lower Risk of Surgical Complications: Avoids risks associated with surgical procedures.
- Immediate Bonding: Skin-to-skin contact with the baby is often possible immediately.
Considerations:
- Pain Management: Options include epidural anesthesia, spinal blocks, or natural pain relief methods.
- Potential for Episiotomy or Tear: Sometimes, a small incision (episiotomy) or natural tearing may occur to assist delivery.